Do You Hook Up Heart Leads on Back Same Way
The ECG is one of the most useful investigations in medicine. Electrodes attached to the chest and/or limbs record small voltage changes as potential difference, which is transposed into a visual tracing
Basic landmarks
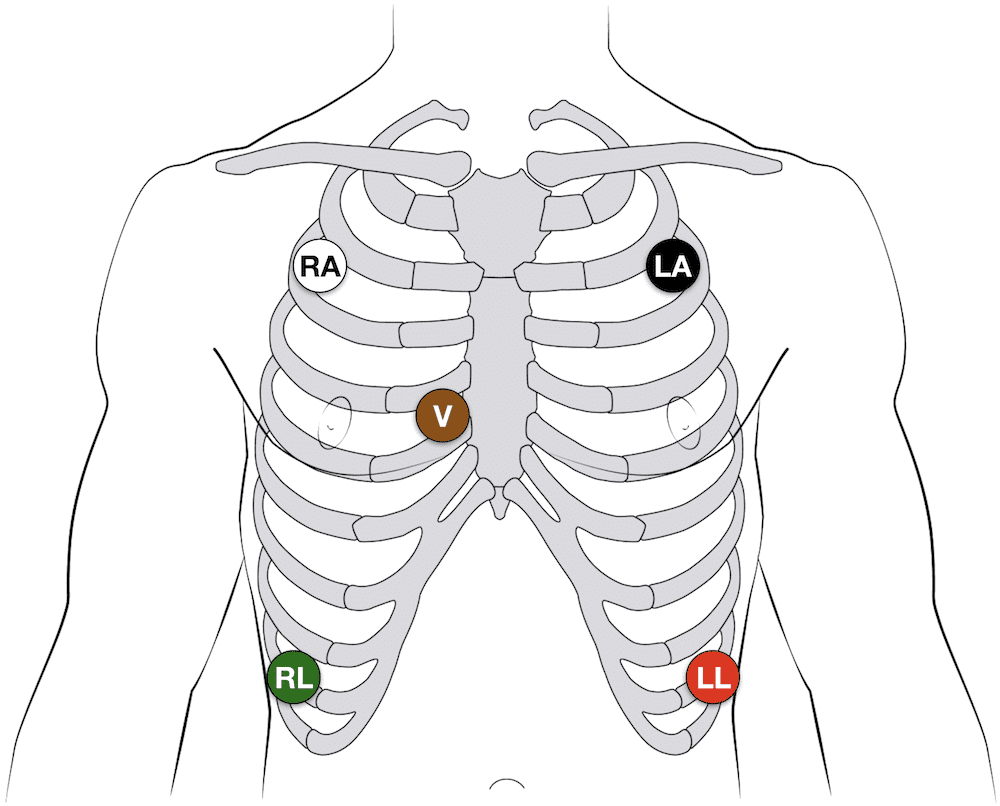
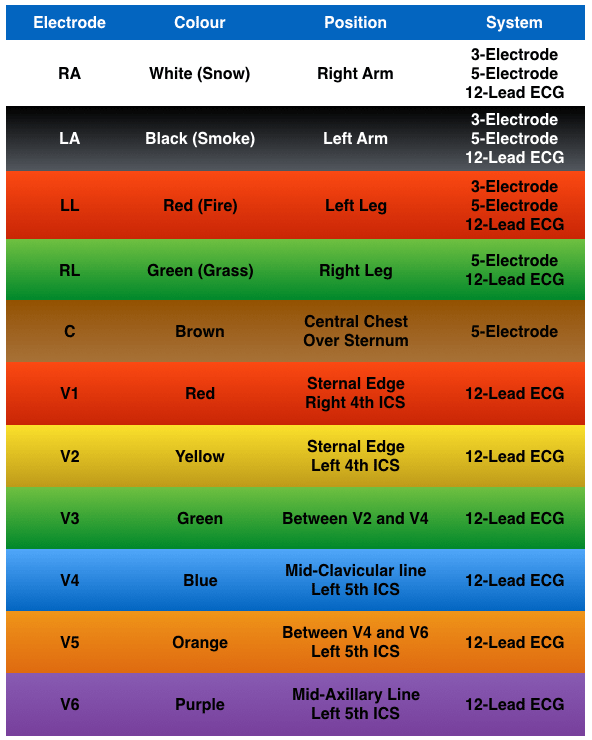
3-electrode system
- Uses3 electrodes (RA, LA and LL)
- Monitor displays the bipolar leads (I, II and III)
- To get best results – Place electrodes on the chest wall equidistant from the heart (rather than the specific limbs)

5-electrode system
- Uses5 electrodes (RA, RL, LA, LL and Chest)
- Monitor displays the bipolar leads (I, II and III)
- AND a single unipolar lead (depending on position of the brown chest lead (positions V1–6))
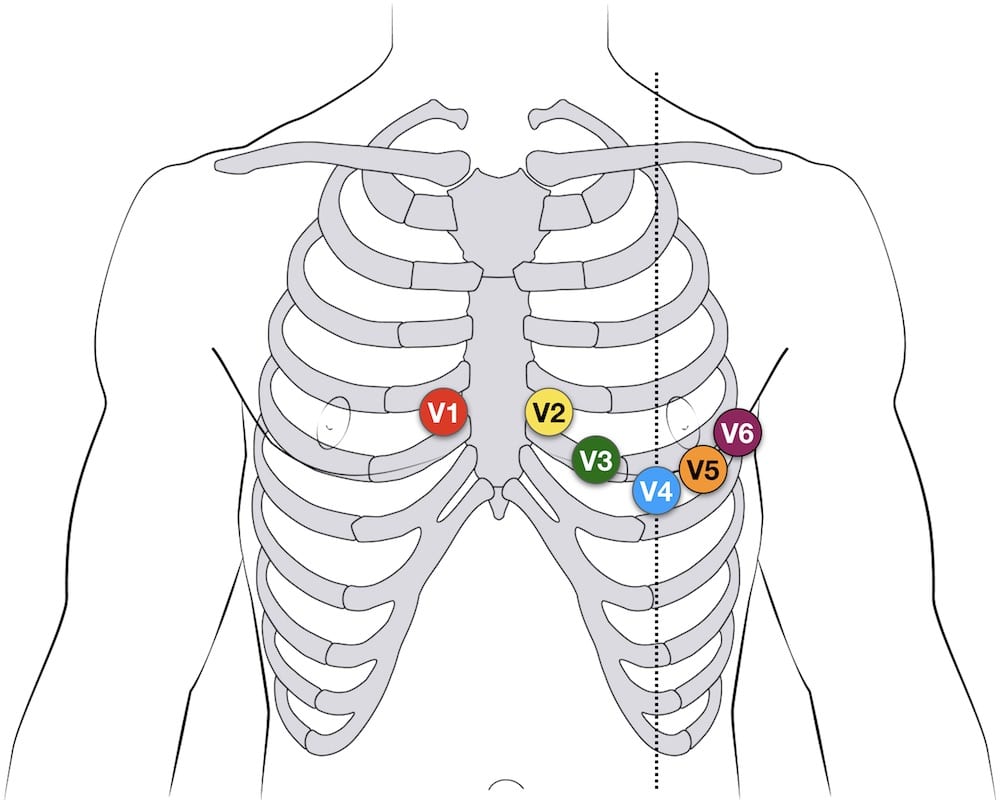
12-lead ECG
- 10 electrodes required to produce 12-lead ECG
- 4 Electrodes on all 4 limbs (RA, LL, LA, RL)6 Electrodes on precordium (V1–6)
- Monitors 12 leads (V1–6), (I, II, III) and (aVR, aVF, aVL)
- Allows interpretation of specific areas of the heart
- Inferior (II, III, aVF)Lateral (I, aVL, V5, V6)Anterior (V1–4)
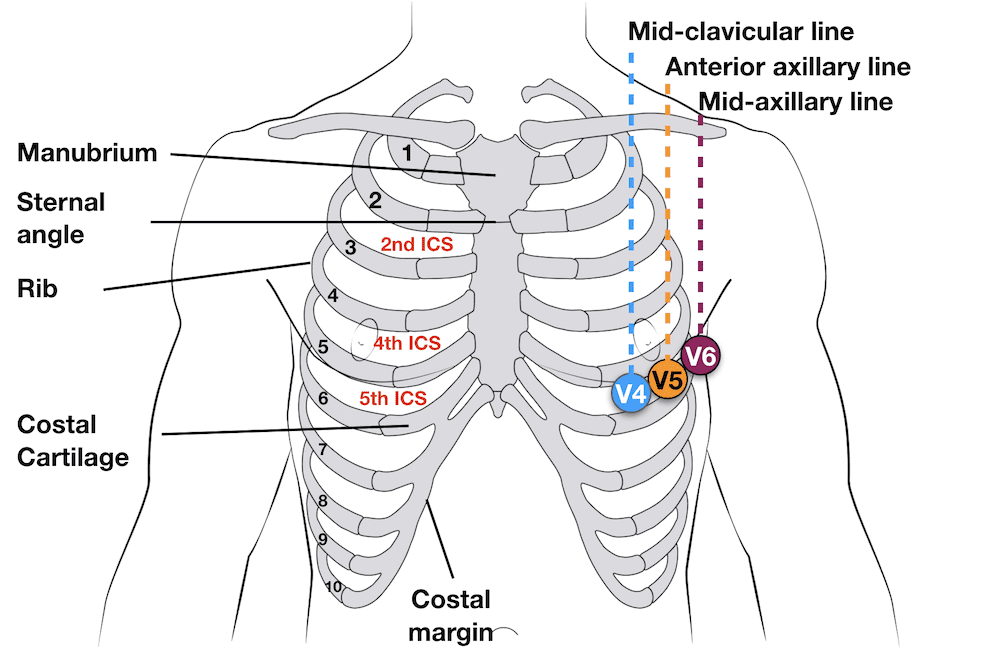
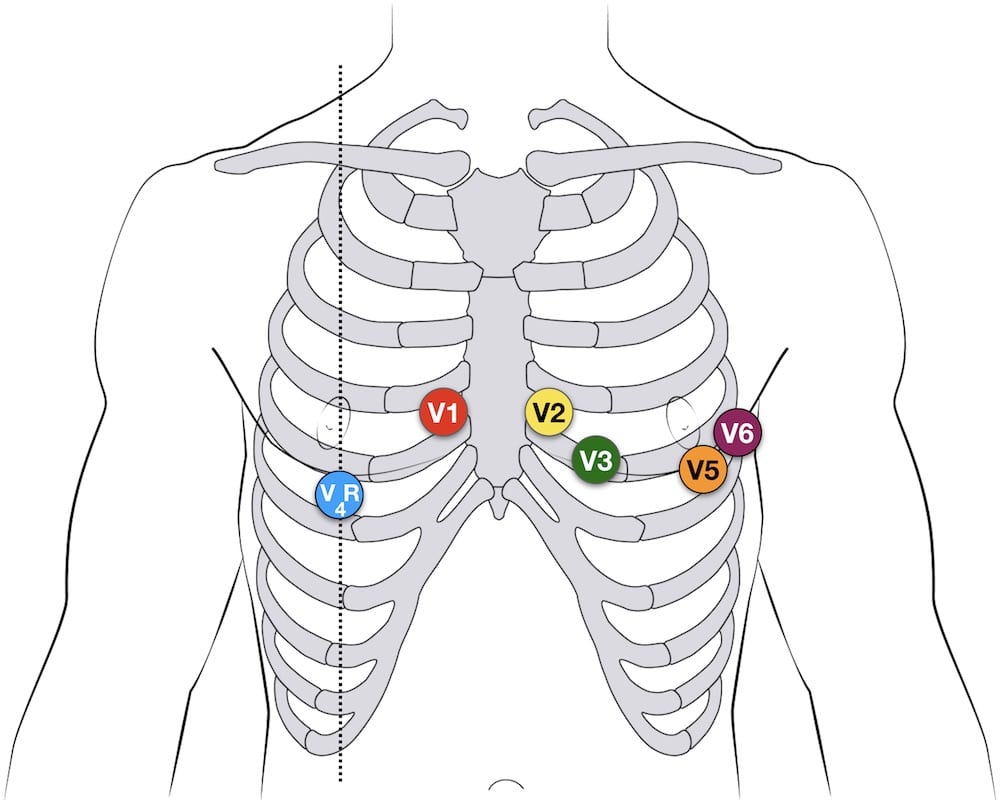
12-lead Precordial lead placement
- V1: 4th intercostal space (ICS), RIGHT margin of the sternum
- V2: 4th ICS along the LEFT margin of the sternum
- V4: 5th ICS, mid-clavicular line
- V3: midway between V2 and V4
- V5: 5th ICS, anterior axillary line (same level as V4)
- V6: 5th ICS, mid-axillary line (same level as V4)
Additional Lead placements
Right sided ECG electrode placement
There are several approaches to recording a right-sided ECG:
- A complete set of right-sided leads is obtained by placing leads V1-6 in a mirror-image position on the right side of the chest (see diagram, below).
- It can be simpler to leave V1 and V2 in their usual positions and just transfer leads V3-6 to the right side of the chest (i.e. V3R to V6R).
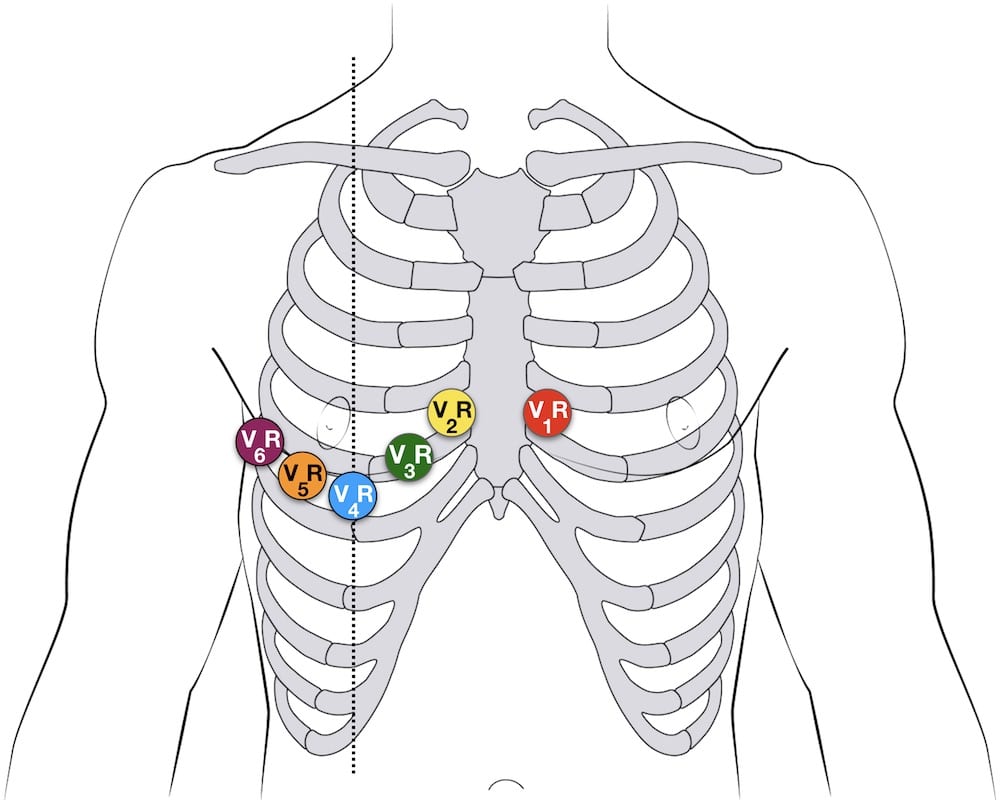
- The most useful lead is V4R, which is obtained by placing the V4 electrode in the 5th right intercostal space in the mid-clavicular line.
- ST elevation in V4R has a sensitivity of 88%, specificity of 78% and diagnostic accuracy of 83% in the diagnosis of RV MI. [see Inferior STEMI]
V4R ECG lead placement
Erhardt et al first described the use of a right sided precordial lead (CR4R or V4R) in the diagnosis of right ventricular infarction which had previously been thought to be electrocardiographically silent. [Single right-sided precordial lead in the diagnosis of right ventricular involvement in inferior myocardial infarction. Am Heart J. 1976]
Posterior leads
Leads V7-9 are placed on the posterior chest wall in the following positions:
- V7 – Left posterior axillary line, in the same horizontal plane as V6.
- V8 – Tip of the left scapula, in the same horizontal plane as V6.
- V9 – Left paraspinal region, in the same horizontal plane as V6.
See Posterior STEMI

Lewis lead (S5-lead)
The Lewis lead configuration can help to detect atrial activity and its relationship to ventricular activity. Named after Welsh cardiologist Sir Thomas Lewis (1881-1945) who first described in 1913. Useful in:
- Observing flutter waves in atrial flutter
- Detecting P waves in wide complex tachyarrhythmia to identify atrioventricular dissociation
Lewis lead placement
- Right Arm (RA) electrode on manubrium
- Left Arm (LA) electrode over 5th ICS, right sternal border.
- Left Leg (LL) electrode over right lower costal margin.
- Monitor Lead I
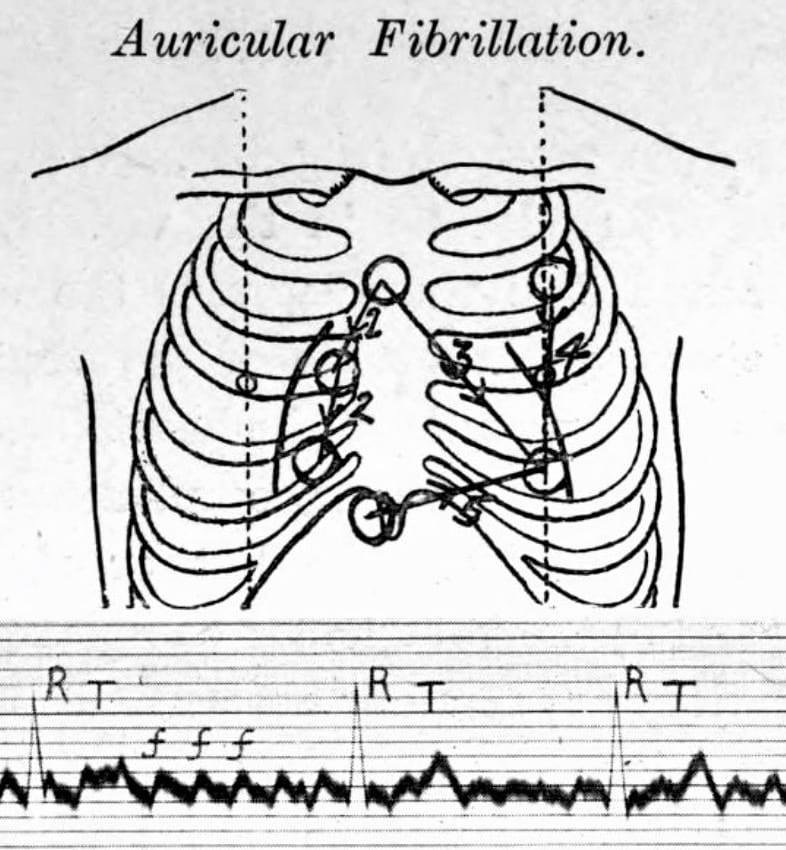
Original Lewis Lead description (1913)
Thomas Lewis (1881-1945) developed and described (1913) his lead configuration to magnify atrial oscillations present during atrial fibrillation [Lewis T. Auricular fibrillation. In: Clinical Electrocardiography. 1913: 86-97]
Fontaine leads
Fontaine bipolar precordial leads (F-ECG) are used to increase the sensitivity of epsilon wave detection. Named after French cardiologist and electrophysiolgist Guy Hugues Fontaine (1936-2018). Leads are placed as shown:
- Right Arm (RA) over the manubrium;
- Left Arm (LA) over the xiphoid process;
- and Left Leg (LL) in the standard V4 position (5th ICS MCL).
Instead of regular leads I, II, and III there are now three bipolar chest leads that are termed FI, FII, and FIII which record the potentials developed in the right ventricle, from the infundibulum to the diaphragm.
The vertical bipolar lead FI, (similar to aVF) magnifies the atrial potentials and can be used to record:
- epsilon waves;
- search for AV dissociation in ventricular tachycardia;
- and to study abnormal atrial rhythms when the P waves are too small on regular leads.

ECG Electrode Guide
ECG Academy Videos
The ECG Lead
The Limb Leads
The Precordial Leads
Related Topics
- ECG Limb Lead Reversals
- Upper Limb Lead reversal
Advanced Reading
Online
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Yellow Belt online course: Become an ECG expert. Medmastery
- Wiesbauer F, Kühn P. ECG Blue Belt online course: Learn to diagnose any rhythm problem. Medmastery
- Rawshani A. Clinical ECG Interpretation ECG Waves
- Smith SW. Dr Smith's ECG blog.
Textbooks
- Mattu A, Tabas JA, Brady WJ. Electrocardiography in Emergency, Acute, and Critical Care. 2e, 2019
- Brady WJ, Lipinski MJ et al. Electrocardiogram in Clinical Medicine. 1e, 2020
- Straus DG, Schocken DD. Marriott's Practical Electrocardiography 13e, 2021
- Hampton J. The ECG Made Practical 7e, 2019
- Grauer K. ECG Pocket Brain (Expanded) 6e, 2014
- Brady WJ, Truwit JD. Critical Decisions in Emergency and Acute Care Electrocardiography 1e, 2009
- Surawicz B, Knilans T. Chou's Electrocardiography in Clinical Practice: Adult and Pediatric 6e, 2008
- Mattu A, Brady W. ECG's for the Emergency Physician Part I 1e, 2003 and Part II
- Chan TC. ECG in Emergency Medicine and Acute Care 1e, 2004
- Smith SW. The ECG in Acute MI. 2002 [PDF]
LITFL Further Reading
- ECG Library Basics – Waves, Intervals, Segments and Clinical Interpretation
- ECG A to Z by diagnosis – ECG interpretation in clinical context
- ECG Exigency and Cardiovascular Curveball – ECG Clinical Cases
- 100 ECG Quiz – Self-assessment tool for examination practice
- ECG Reference SITES and BOOKS – the best of the rest
ECG LIBRARY
Electrocardiogram
Mike Cadogan
Emergency physician MA (Oxon) MBChB (Edin) FACEM FFSEM with a passion for rugby; medical history; medical education; and asynchronous learning #FOAMed evangelist. Co-founder and CTO of Life in the Fast lane | Eponyms | Books | Twitter |
Do You Hook Up Heart Leads on Back Same Way
Source: https://litfl.com/ecg-lead-positioning/
0 Response to "Do You Hook Up Heart Leads on Back Same Way"
Post a Comment